Liability accounts are an essential aspect of any organization’s financial statements. They represent the debts or obligations that the company owes retained earnings balance sheet to others, and they are used to track the company’s financial health. Auditing liability accounts is an important part of the audit process, as these accounts represent the company’s financial obligations.
Application Management
Similarly, the interest liability related to a long-term loan payable within the next year will come under current liabilities. Short-term debt is any financial obligation that matures within 12 months. Short-term debt includes short-term bank loans, lines of credit, and short-term leases. Automated accounts payable systems, like BILL, make it much easier for businesses to meet short-term obligations to vendors and suppliers. Supplies payable Outsource Invoicing are amounts owed for supplies received but not yet paid for. Keeping track of these liabilities helps manage cash flow and inventory.
Financial Liabilities Definition
- Examples of contingent liabilities are the outcome of a lawsuit, a government investigation, or the threat of expropriation.
- Internal – It is payable to internal parties such as promoters (owners), employees etc.
- Examples of common liabilities include accounts payable, accrued expenses, wages payable, and short-term loans.
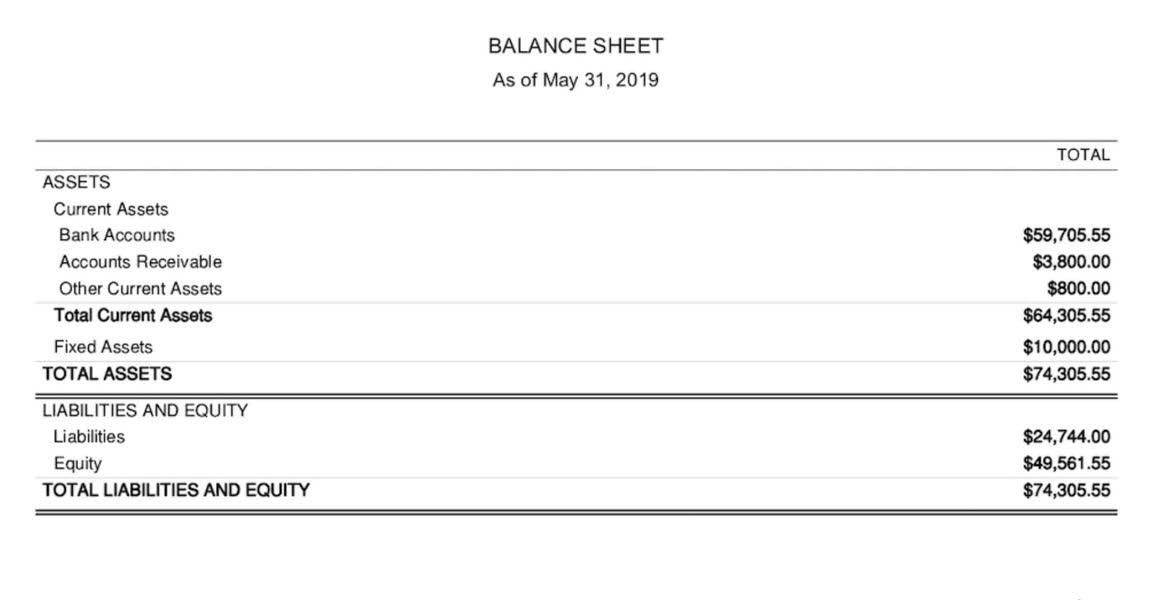
- The flip side of liabilities is assets — resources the company uses to generate income.
- Almost all of the financial liabilities can be listed on the entity’s balance sheet.
Liability in accounting refers to a company’s financial obligations, including debts like loans and accounts payable, categorised as current or long-term liabilities. Unlike expenses, liabilities involve owed amounts that have yet to be paid. Non-current liabilities are debts or obligations you owe that are not due within a year.
Current Portion of Long-Term Debt

Legal fees payable include fees incurred but not yet paid for legal services. Managing these payments is essential for budgeting and financial planning. A corporation, for example, has incurred $7,000 in legal fees related to a lawsuit, which will be paid next month. The primary classification of liabilities is according to their due date.
How to calculate total assets
Unearned revenue is money received or paid to a company for a product or service that has yet to be delivered or provided. Unearned revenue is listed as a current liability because it’s a type of debt owed to the customer. Once the service or product has been provided, the unearned revenue gets recorded as revenue on the income statement. In its most basic sense, a liability is a requirement that must be fulfilled.
Creditworthiness and Lending Decisions

Advance payments received for goods or services that haven’t liability examples been provided yet. Loans that are due for repayment within a year, which are used to fund day-to-day operations. Businesses often owe money to suppliers for goods or services received but not yet paid for. Notice that Current Liabilities is explicitly labeled and has its own subtotal.
- Unsettled medical expenses for treatments and healthcare services.
- You’ve learned their meaning, types, and key examples, like loans or accounts payable.
- If they have enough assets, they can get enough cash by selling them off and paying the debt as it comes due.
- Advance payments received for goods or services that haven’t been provided yet.
- They are short-term liabilities usually arisen out of business activities.
For instance, a company must pay $5,000 in fees for financial consulting services within the next month. Contingent liabilities are a special type of debt or obligation that may or may not happen in the future. These liabilities are contingent (or dependent on) certain events. The most common example of a contingent liability is legal costs related to the outcome of a lawsuit. For example, if the company wins the case and doesn’t need to pay any money, the company doesn’t incur the contingent liability.

You would classify a liability as a current liability if you expect to liquidate the obligation within one year. If there is a long-term note or bond payable, that portion of it due for payment within the next year is classified as a current liability. Most types of liabilities are classified as current liabilities, including accounts payable, accrued liabilities, and wages payable.
Subtracting the liabilities from the assets provides a measure of the company’s equity or net worth. Corporate finance essentials payable refers to short-term financial obligations arising from corporate finance activities. Managing these payables is key to maintaining financial stability.
